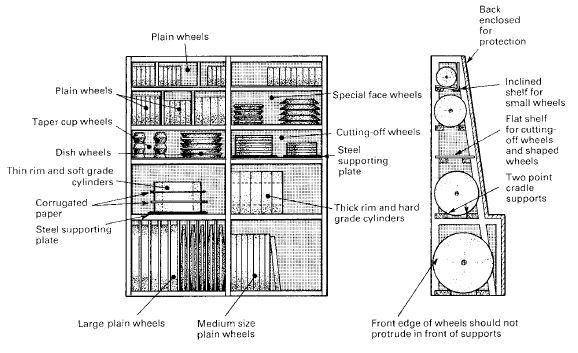
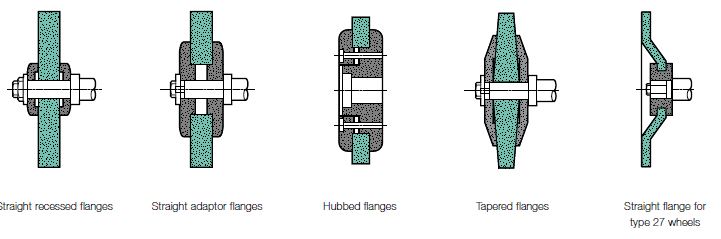
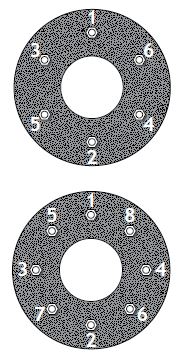
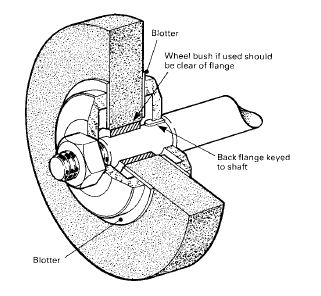
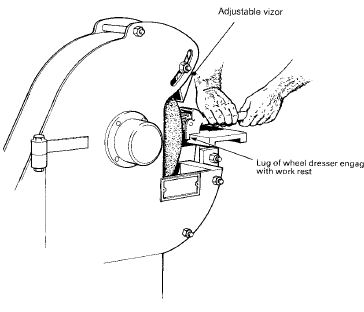
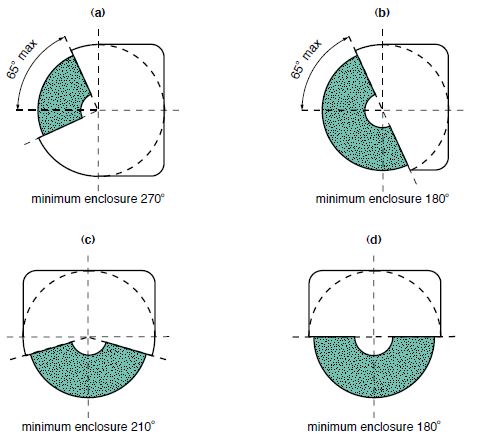
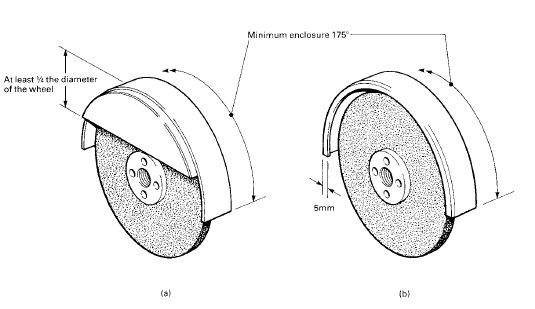
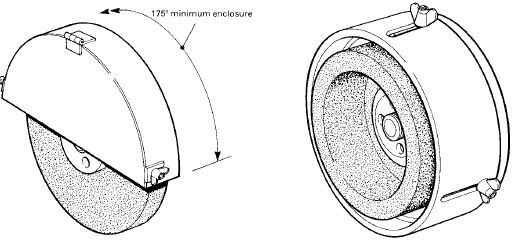
Portable, bench or floor mounted power tools and equipment need routine maintenance, inspection and adjustments to ensure safe operation. Tool bits, blades and other changeable parts must be kept sharp and free from damage. Electrical systems, belts & pulleys and gears must be properly guarded to prevent exposing employees to hazards.

Tool General Safety Precautions:
Employees who use hand and power tools and who are exposed to the hazards of falling, flying, abrasive and splashing objects, or exposed to harmful dusts, fumes, mists, vapors, or gases must be provided with the particular personal equipment necessary to protect them from the hazard. All hazards involved in the use of tools can be prevented by following five basic safety rules:
- Keep all tools in good condition with regular maintenance.

- Use the right tool for the job.
- Examine each tool for damage before use.
- Operate according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Provide and use the proper protective equipment.
Hand Tools:
Hand tools are non-powered. They include anything from axes to wrenches. The greatest hazards posed by hand tools result from misuse and improper maintenance.Some examples:
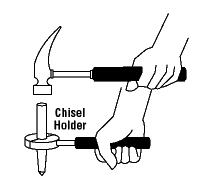
• Using a screwdriver as a chisel may cause the tip of the screwdriver to break and fly, hitting the user or other employees.
• If a wooden handle on a tool such as a hammer or an axe is loose, splintered, or cracked, the head of the tool may fly off and strike the user or another worker.
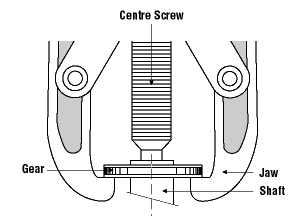
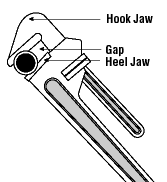
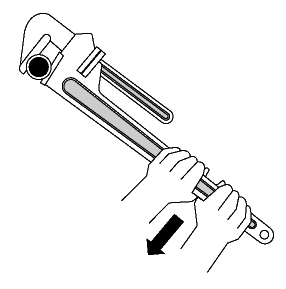
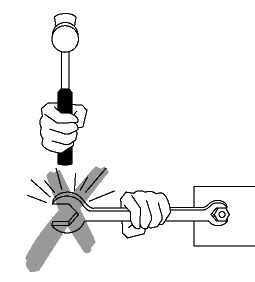
• A wrench must not be used if its jaws are sprung, because it might slip.
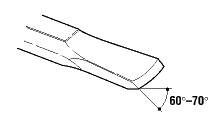
• Impact tools such as chisels, wedges, or drift pins are unsafe if they have mushroomed heads.
The heads might shatter on impact, sending sharp fragments flying.Appropriate personal protective equipment, e.g., safety goggles, gloves, etc., should be worn due to hazards that may be encountered while using portable power tools and hand tools.Floors shall be kept as clean and dry as possible to prevent accidental slips with or around dangerous hand tools.Around flammable substances, sparks produced by iron and steel hand tools can be a dangerous ignition source. Where this hazard exists, spark-resistant tools made from brass, plastic, aluminum, or wood will provide for safety.
Basic tips when using hand tools:
- Always provide training on how to choose the right tool for the job, how to correctly use each tool, and how to identify when tools need repair.
- Select the right tool for the job. Substitutes increase the chance of having an accident.
- Use tools designed to allow wrist to stay straight. Avoid using hand tools with your wrist bent.
- Ensure that employees are properly trained in the safe use of hand tools.
- Use good quality tools.

- Keep tools in good condition at all times.
- Inspect tools for defects before use. Replace or repair defective tools.
- Keep cutting tools sharp and cover sharp edges with suitable covering to protect the tool and to prevent injuries from unintended contact.
- Replace cracked, splintered, or broken handles on files, hammers, screwdrivers, or sledges.
- Ensure that the handles of tools like hammers and axes fit tightly into the head of the tool.
- Replace worn jaws on wrenches, pipe tools and pliers.
- Redress burred or mushroomed heads of striking tools.
- Pull on a wrench or pliers. Never push unless you hold the tool with your palm open.
- Point sharp tools (e.g., saws, chisels, knives) laying on benches away from aisles and handles should not extend over the edge of the bench top.
- Maintain tools carefully. Keep them clean and dry, and store them properly after each use.
- Carry tools in a sturdy tool box to and from the work site.
- Wear safety glasses or goggles, or a face shield (with safety glasses or goggles) and well-fitting gloves appropriate for the hazards to which you may be exposed when doing various tasks.
- Keep the work environment clean and tidy to avoid clutter which may cause accidents.
- Use a heavy belt or apron and hang tools at your sides, not behind your back.
Power Tool Precautions:
Power tools can be hazardous when improperly used. There are several types of power tools, based on the power source they use: electric, pneumatic, liquid fuel, hydraulic, and powder-actuated.The following general precautions should be observed by power tool users:
The following general precautions shall be observed by power tool users:
- Never carry a tool by the cord or hose;
- Never remove prongs from any cords;
- Never stand in or near water when using tools;
- Always use a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) with electrical tools if working in a wet environment;
- Never “yank” the cord or the hose to disconnect it from the receptacle;

- Keep cords and hoses away from heat, oil and sharp edges;
- Replace all frayed and/or damaged extension cords. Do not try to tape cords;
- Disconnect tools when not in use, before servicing and when changing accessories such as blades, bits and cutters;
- All observers shall be kept at a safe distance away from the work area;
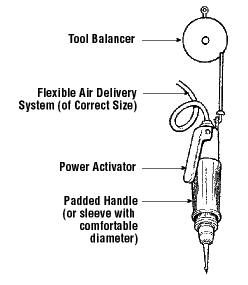
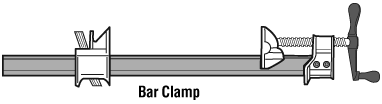
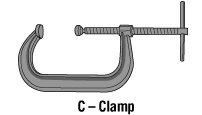
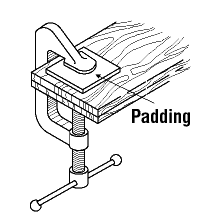
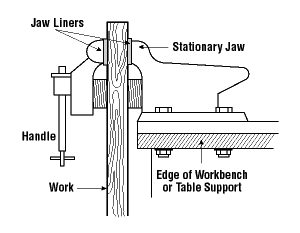
- Secure work with clamps or a vise, freeing both hands to operate the tool;
- Avoid accidental starting. The worker shall not hold a finger on the switch button while carrying a plugged-in tool;
- Tools shall be maintained with care. They shall be kept sharp and clean for the best performance. Follow instructions in the user’s manual for maintenance, lubricating and changing accessories;
- Maintain good footing and balance;
- Avoid loose fitting clothes, ties or jewelry such as bracelets, watches or rings, which can become caught in moving parts;
- Use tools that are either double-insulated or grounded (three-pronged);
- Keep work area well lit when operating electric tools;
- Ensure that cords and hoses do not pose as a tripping hazard; and
- All portable electric tools that are damaged shall be removed from use and tagged “Do Not Use”. This shall be done by supervisors and/or employees.